Reference Architecture with Terraform: VM-Series in AWS, Isolated Design Model, Common NGFW option with Autoscaling
Palo Alto Networks produces several validated reference architecture design and deployment documentation guides, which describe well-architected and tested deployments. When deploying VM-Series in a public cloud, the reference architectures guide users toward the best security outcomes, whilst reducing rollout time and avoiding common integration efforts. The Terraform code presented here will deploy Palo Alto Networks VM-Series firewalls in AWS based on the centralized design; for a discussion of other options, please see the design guide from the reference architecture guides.
Reference Architecture Design
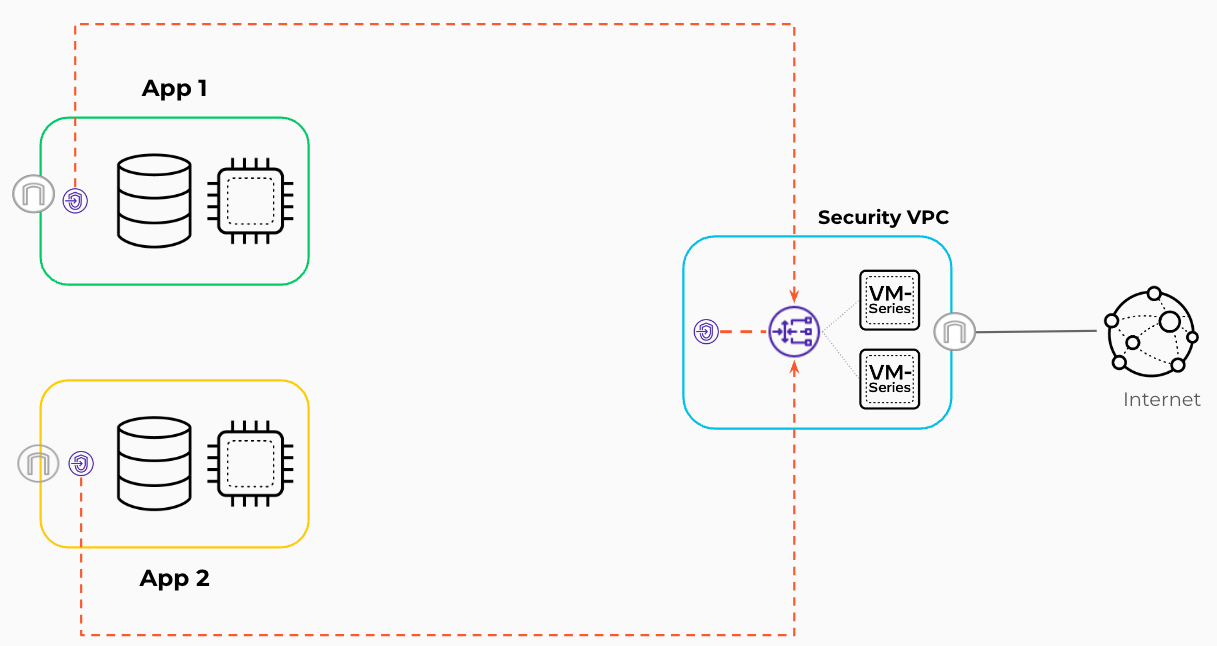
This code implements:
- an isolated design, which secures outbound and inbound traffic flows using AWS Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB). Application resources are segmented across multiple VPCs that distribute traffic to the dedicated VPC for security services where the VM-Series are deployed.
Detailed Architecture and Design
Isolated Design
The Isolated Design model centralizes the security instances in a dedicated security VPC, while providing one or more isolated VPCs inbound and outbound security services. This design leverages a VPC dedicated to security. In the security VPC, you deploy the VM-Series firewalls, in separate availability zones, and a GWLB to distribute traffic to the firewalls. This design uses overlay routing for outbound security on the VM-Series firewalls. Outbound traffic from instances in the isolated VPCs uses the PrivateLink connections from GWLB endpoints in the applications. VPCs to the GWLB in the security VPC to egress the AWS environment through the VM-Series firewalls.
Inbound traffic originates outside the VPC and is destined to applications or services hosted within your VPCs, such as web servers. This design uses the GWLB and VM-Series firewalls in the security VPC, with GWLB endpoints in the application VPCs for the transparent inspection of inbound traffic.
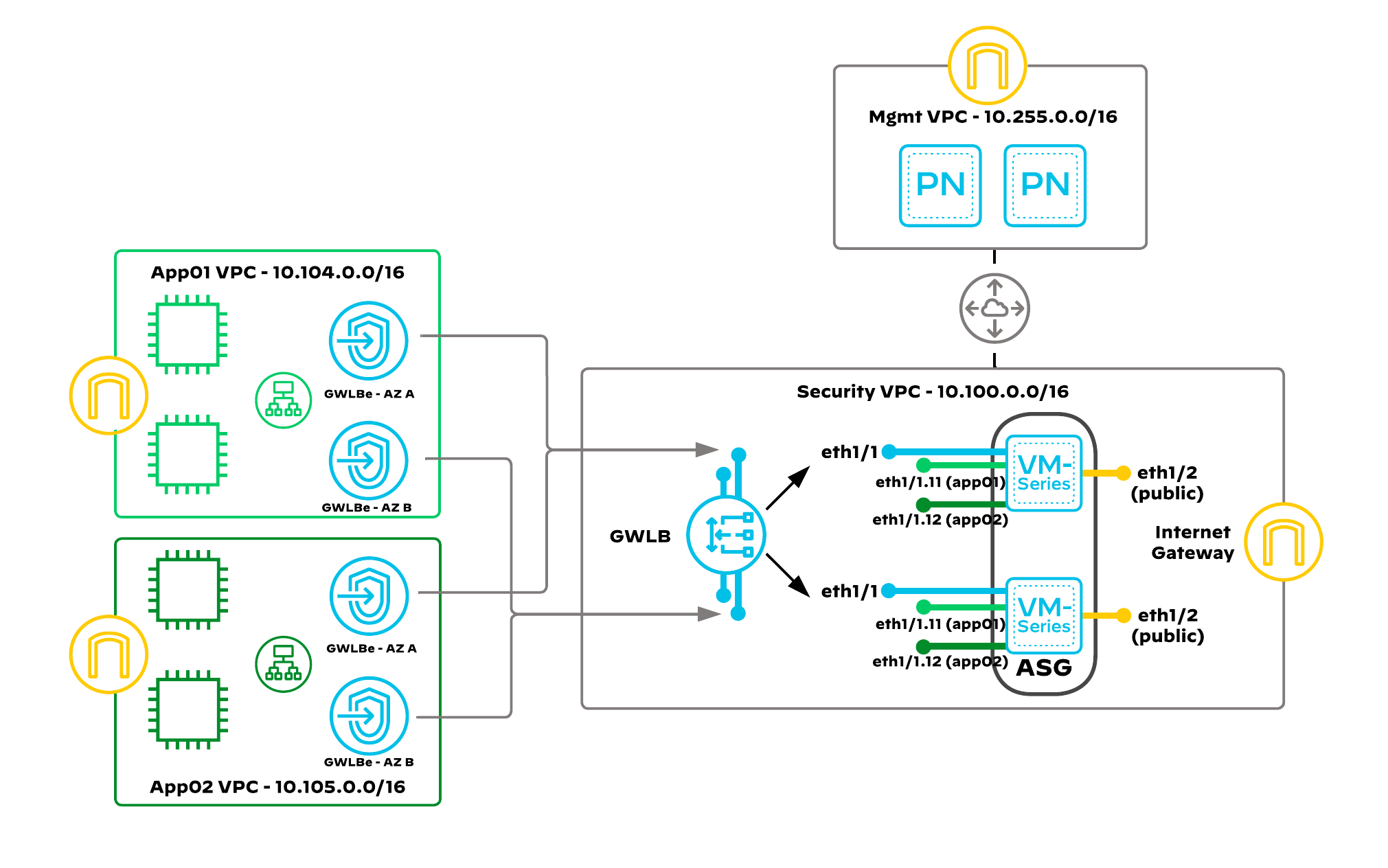
Auto Scaling VM-Series
Auto scaling: Public-cloud environments focus on scaling out a deployment instead of scaling up. This architectural difference stems primarily from the capability of public-cloud environments to dynamically increase or decrease the number of resources allocated to your environment. Using native AWS services like CloudWatch, auto scaling groups (ASG) and VM-Series automation features, the guide implements VM-Series that will scale in and out dynamically, as your protected workload demands fluctuate. The VM-Series firewalls are deployed in an auto scaling group, and are automatically registered to a Gateway Load Balancer. While bootstrapping the VM-Series, there are associations made automatically between VM-Series subinterfaces and the GWLB endpoints. Each VM-Series contains multiple network interfaces created by an AWS Lambda function.
Prerequisites
The following steps should be followed before deploying the Terraform code presented here.
- Deploy Panorama e.g. by using Panorama example
- Prepare device group, template, template stack in Panorama
- Download and install plugin
sw_fw_licensefor managing licenses - Configure bootstrap definition and license manager
- Configure license API key
- Configure security rules and NAT rules for outbound traffic
- Configure interface management profile to enable health checks from GWLB
- Configure network interfaces and subinterfaces, zones and virtual router in template
- Configure static routes with path monitoring
- Configure VPC peering between VPC with Panorama and VPC with VM-Series in autoscaling group (after deploying that example)
Details - static routes with path monitoring
Using multiple template stacks, one for each AZ complicates autoscaling and the Panorama Licensing plugin configuration. The virtual router (VR) configuration combined with path monitoring outlined below avoids using AZ-specific template stacks and variables.
Virtual Router Configuration
- Create static routes for all internally routed CIDRs
- Set the next hop to the default gateway IP of the trust subnet of the corresponding availability zone, which the firewall is connected to.
- Set a unique metric value per AZ so that it doesn't overlap with other routes with the same destinations.
- Enable Path Monitoring for the route.
- Source IP: DHCP
- Destination IP: Next Hop IP of the subnet of the corresponding AZ.
The AWS NACL applied to the trust subnets blocks the path monitor from pinging default gateways of the trust subnets in the other availability zones. This will cause the firewall to remove all routes that don't apply to the Availability zone it is in.
Below there is shown example of VR configuration with static routes and path monitoring:
| Name | Destination | Next Hop | Metric | Path Monitor Destination IP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| app1_az1 | 10.104.0.0/16 | 10.100.1.1 | 11 | 10.100.1.1 |
| app2_az1 | 10.105.0.0/16 | 10.100.1.1 | 11 | 10.100.1.1 |
| app1_az2 | 10.104.0.0/16 | 10.100.65.1 | 12 | 10.100.65.1 |
| app2_az2 | 10.105.0.0/16 | 10.100.65.1 | 12 | 10.100.65.1 |
| health_az1 | 10.100.0.0/16 | 10.100.1.1 | 11 | 10.100.1.1 |
| health_az2 | 10.100.0.0/16 | 10.100.65.1 | 12 | 10.100.65.1 |
An example XML configuration snippet (for PANOS 10.2.3) of the described configuration can be found here, which after importing to Panorama, can be merged using the command:
load config partial mode merge from-xpath /config/devices/entry/template/entry[@name='asg'] to-xpath /config/devices/entry/template/entry[@name='asg'] from template-asg-path-monitoring.xml
Spoke VMs
For the proposed example, the Spoke VMs are supporting ssm-agent. In addition, the VM user_data contains an installation of httpd service.
To enable access from the session manager, the Internet connection for a public endpoint is required.
Usage
- Copy
example.tfvarsintoterraform.tfvars - Review
terraform.tfvarsfile, especially with lines commented by# TODO: update here - Initialize Terraform:
terraform init - Prepare plan:
terraform plan - Deploy infrastructure:
terraform apply -auto-approve - Destroy infrastructure if needed:
terraform destroy -auto-approve
Additional Reading
Lambda function
Lambda function is used to handle correct lifecycle action:
- instance launch or
- instance terminate
In case of creating VM-Series, there are performed below actions, which cannot be achieved in AWS launch template:
- change setting
source_dest_checkfor first network interface (data plane) - setup additional network interfaces (with optional possibility to attach EIP)
In case of destroying VM-Series, there is performed below action:
- clean EIP
Moreover having Lambda function executed while scaling out or in gives more options for extension e.g. delicesning VM-Series just after terminating instance.
Autoscaling
AWS Auto Scaling monitors VM-Series and automatically adjusts capacity to maintain steady, predictable performance at the lowest possible cost. For autoscaling there are 10 metrics available from vmseries plugin:
DataPlaneCPUUtilizationPctDataPlanePacketBufferUtilizationpanGPGatewayUtilizationPctpanGPGWUtilizationActiveTunnelspanSessionActivepanSessionConnectionsPerSecondpanSessionSslProxyUtilizationpanSessionThroughputKbpspanSessionThroughputPpspanSessionUtilization
Using that metrics there can be configured different scaling plans. Below there are some examples, which can be used. All examples are based on target tracking configuration in scaling plan. Below code is already embedded into asg module:
scaling_instruction {
max_capacity = var.max_size
min_capacity = var.min_size
resource_id = format("autoScalingGroup/%s", aws_autoscaling_group.this.name)
scalable_dimension = "autoscaling:autoScalingGroup:DesiredCapacity"
service_namespace = "autoscaling"
target_tracking_configuration {
customized_scaling_metric_specification {
metric_name = var.scaling_metric_name
namespace = var.scaling_cloudwatch_namespace
statistic = var.scaling_statistic
}
target_value = var.scaling_target_value
}
}
Using metrics from vmseries plugin we can defined multiple scaling configurations e.g.:
- based on number of active sessions:
metric_name = "panSessionActive"
target_value = 75
statistic = "Average"
- based on data plane CPU utilization and average value above 75%:
metric_name = "DataPlaneCPUUtilizationPct"
target_value = 75
statistic = "Average"
- based on data plane packet buffer utilization and max value above 80%
metric_name = "DataPlanePacketBufferUtilization"
target_value = 80
statistic = "Maximum"
Reference
Requirements
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| terraform | >= 1.5.0, < 2.0.0 |
| aws | ~> 5.17 |
Providers
| Name | Version |
|---|---|
| aws | ~> 5.17 |
Modules
| Name | Source | Version |
|---|---|---|
| gwlb | ../../modules/gwlb | n/a |
| gwlbe_endpoint | ../../modules/gwlb_endpoint_set | n/a |
| public_alb | ../../modules/alb | n/a |
| public_nlb | ../../modules/nlb | n/a |
| subnet_sets | ../../modules/subnet_set | n/a |
| vm_series_asg | ../../modules/asg | n/a |
| vpc | ../../modules/vpc | n/a |
| vpc_routes | ../../modules/vpc_route | n/a |
Resources
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
| aws_iam_instance_profile.spoke_vm_iam_instance_profile | resource |
| aws_iam_instance_profile.vm_series_iam_instance_profile | resource |
| aws_iam_role.spoke_vm_ec2_iam_role | resource |
| aws_iam_role.vm_series_ec2_iam_role | resource |
| aws_iam_role_policy.vm_series_ec2_iam_policy | resource |
| aws_iam_role_policy_attachment.spoke_vm_iam_instance_policy | resource |
| aws_instance.spoke_vms | resource |
| aws_vpc_peering_connection.this | resource |
| aws_ami.this | data source |
| aws_caller_identity.this | data source |
| aws_ebs_default_kms_key.current | data source |
| aws_kms_key.current | data source |
| aws_partition.this | data source |
Inputs
| Name | Description | Type | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| global_tags | Global tags configured for all provisioned resources | any | n/a | yes |
| gwlb_endpoints | A map defining GWLB endpoints. Following properties are available: - name: name of the GWLB endpoint- gwlb: key of GWLB- vpc: key of VPC- subnet_group: key of the subnet_group- act_as_next_hop: set to true if endpoint is part of an IGW route table e.g. for inbound traffic- from_igw_to_vpc: VPC to which traffic from IGW is routed to the GWLB endpoint- from_igw_to_subnet_group : subnet_group to which traffic from IGW is routed to the GWLB endpointExample:gwlb_endpoints = { security_gwlb_eastwest = { name = "eastwest-gwlb-endpoint" gwlb = "security_gwlb" vpc = "security_vpc" subnet_group = "gwlbe_eastwest" act_as_next_hop = false } } | map(object({ name = string gwlb = string vpc = string subnet_group = string act_as_next_hop = bool from_igw_to_vpc = optional(string) from_igw_to_subnet_group = optional(string) })) | {} | no |
| gwlbs | A map defining Gateway Load Balancers. Following properties are available: - name: name of the GWLB- vpc: key of the VPC- subnet_group: key of the subnet_groupExample:gwlbs = { security_gwlb = { name = "security-gwlb" vpc = "security_vpc" subnet_group = "gwlb" } } | map(object({ name = string vpc = string subnet_group = string })) | {} | no |
| name_prefix | Prefix used in names for the resources (VPCs, EC2 instances, autoscaling groups etc.) | string | n/a | yes |
| panorama_connection | A object defining VPC peering and CIDR for Panorama. Following properties are available: - security_vpc: key of the security VPC- peering_vpc_id: ID of the VPC for Panorama- vpc_cidr: CIDR of the VPC, where Panorama is deployedExample:panorama = { security_vpc = "security_vpc" peering_vpc_id = "vpc-1234567890" vpc_cidr = "10.255.0.0/24" } | object({ security_vpc = string peering_vpc_id = string vpc_cidr = string }) | null | no |
| region | AWS region used to deploy whole infrastructure | string | n/a | yes |
| spoke_albs | A map defining Application Load Balancers deployed in spoke VPCs. Following properties are available: - rules: Rules defining the method of traffic balancing- vms: Instances to be the target group for ALB- vpc: The VPC in which the load balancer is to be run- subnet_group: The subnet_groups in which the Load Balancer is to be run- security_gropus: Security Groups to be associated with the ALB | map(object({ rules = any vms = list(string) vpc = string subnet_group = string security_groups = string })) | n/a | yes |
| spoke_nlbs | A map defining Network Load Balancers deployed in spoke VPCs. Following properties are available: - vpc: key of the VPC- subnet_group: key of the subnet_group- vms: keys of spoke VMsExample:spoke_lbs = { "app1-nlb" = { vpc = "app1_vpc subnet_group = "app1_lb" vms = ["app1_vm01", "app1_vm02"] } } | map(object({ vpc = string subnet_group = string vms = list(string) })) | {} | no |
| spoke_vms | A map defining VMs in spoke VPCs. Following properties are available: - az: name of the Availability Zone- vpc: name of the VPC (needs to be one of the keys in map vpcs)- subnet_group: key of the subnet_group- security_group: security group assigned to ENI used by VM- type: EC2 type VMExample:spoke_vms = { "app1_vm01" = { az = "eu-central-1a" vpc = "app1_vpc" subnet_group = "app1_vm" security_group = "app1_vm" type = "t2.micro" } } | map(object({ az = string vpc = string subnet_group = string security_group = string type = string })) | {} | no |
| ssh_key_name | Name of the SSH key pair existing in AWS key pairs and used to authenticate to VM-Series or test boxes | string | n/a | yes |
| vmseries_asgs | A map defining Autoscaling Groups with VM-Series instances. Following properties are available: - bootstrap_options: VM-Seriess bootstrap options used to connect to Panorama- panos_version: PAN-OS version used for VM-Series- ebs_kms_id: alias for AWS KMS used for EBS encryption in VM-Series- vpc: key of VPC- gwlb: key of GWLB- zones: zones for the Autoscaling Group to be built in- interfaces: configuration of network interfaces for VM-Series used by Lamdba while provisioning new VM-Series in autoscaling group- subinterfaces: configuration of network subinterfaces used to map with GWLB endpoints- asg: the number of Amazon EC2 instances that should be running in the group (desired, minimum, maximum)- scaling_plan: scaling plan with attributes- enabled: true if automatic dynamic scaling policy should be created- metric_name: name of the metric used in dynamic scaling policy- estimated_instance_warmup: estimated time, in seconds, until a newly launched instance can contribute to the CloudWatch metrics- target_value: target value for the metric used in dynamic scaling policy- statistic: statistic of the metric. Valid values: Average, Maximum, Minimum, SampleCount, Sum- cloudwatch_namespace: name of CloudWatch namespace, where metrics are available (it should be the same as namespace configured in VM-Series plugin in PAN-OS)- tags: tags configured for dynamic scaling policy- launch_template_version: launch template version to use to launch instances- instance_refresh: instance refresh for ASG defined by several attributes (please README for module asg for more details)Example:vmseries_asgs = { main_asg = { bootstrap_options = { mgmt-interface-swap = "enable" plugin-op-commands = "panorama-licensing-mode-on,aws-gwlb-inspect:enable,aws-gwlb-overlay-routing:enable" # TODO: update here panorama-server = "" # TODO: update here auth-key = "" # TODO: update here dgname = "" # TODO: update here tplname = "" # TODO: update here dhcp-send-hostname = "yes" # TODO: update here dhcp-send-client-id = "yes" # TODO: update here dhcp-accept-server-hostname = "yes" # TODO: update here dhcp-accept-server-domain = "yes" # TODO: update here } panos_version = "10.2.3" # TODO: update here ebs_kms_id = "alias/aws/ebs" # TODO: update here vpc = "security_vpc" gwlb = "security_gwlb" zones = { "01" = "us-west-1a" "02" = "us-west-1b" } interfaces = { private = { device_index = 0 security_group = "vmseries_private" subnet_group = "private" create_public_ip = false source_dest_check = false } mgmt = { device_index = 1 security_group = "vmseries_mgmt" subnet_group = "mgmt" create_public_ip = true source_dest_check = true } public = { device_index = 2 security_group = "vmseries_public" subnet_group = "public" create_public_ip = false source_dest_check = false } } subinterfaces = { inbound = { app1 = { gwlb_endpoint = "app1_inbound" subinterface = "ethernet1/1.11" } app2 = { gwlb_endpoint = "app2_inbound" subinterface = "ethernet1/1.12" } } outbound = { only_1_outbound = { gwlb_endpoint = "security_gwlb_outbound" subinterface = "ethernet1/1.20" } } eastwest = { only_1_eastwest = { gwlb_endpoint = "security_gwlb_eastwest" subinterface = "ethernet1/1.30" } } } asg = { desired_cap = 0 min_size = 0 max_size = 4 lambda_execute_pip_install_once = true } scaling_plan = { enabled = true metric_name = "panSessionActive" estimated_instance_warmup = 900 target_value = 75 statistic = "Average" cloudwatch_namespace = "asg-vmseries" tags = { ManagedBy = "terraform" } } launch_template_version = "1" instance_refresh = { strategy = "Rolling" preferences = { checkpoint_delay = 3600 checkpoint_percentages = [50, 100] instance_warmup = 1200 min_healthy_percentage = 50 skip_matching = false auto_rollback = false scale_in_protected_instances = "Ignore" standby_instances = "Ignore" } triggers = [] } } } | map(object({ bootstrap_options = object({ mgmt-interface-swap = string plugin-op-commands = string panorama-server = string auth-key = optional(string) vm-auth-key = optional(string) dgname = string tplname = optional(string) dhcp-send-hostname = string dhcp-send-client-id = string dhcp-accept-server-hostname = string dhcp-accept-server-domain = string authcodes = optional(string) vm-series-auto-registration-pin-id = optional(string) vm-series-auto-registration-pin-value = optional(string) }) panos_version = string ebs_kms_id = string vpc = string gwlb = string zones = map(any) interfaces = map(object({ device_index = number security_group = string subnet_group = string create_public_ip = bool source_dest_check = bool })) subinterfaces = map(map(object({ gwlb_endpoint = string subinterface = string }))) asg = object({ desired_cap = number min_size = number max_size = number lambda_execute_pip_install_once = bool }) scaling_plan = object({ enabled = bool metric_name = string estimated_instance_warmup = number target_value = number statistic = string cloudwatch_namespace = string tags = map(string) }) launch_template_version = string instance_refresh = object({ strategy = string preferences = object({ checkpoint_delay = number checkpoint_percentages = list(number) instance_warmup = number min_healthy_percentage = number skip_matching = bool auto_rollback = bool scale_in_protected_instances = string standby_instances = string }) triggers = list(string) }) })) | {} | no |
| vpcs | A map defining VPCs with security groups and subnets. Following properties are available: - name: VPC name- cidr: CIDR for VPC- nacls: map of network ACLs- security_groups: map of security groups- subnets: map of subnets with properties:- az: availability zone- subnet_group: identity of the same purpose subnets group such as management- nacl: key of NACL (can be null)- routes: map of routes with properties:- vpc: key of VPC- subnet_group: key of subnet_group- next_hop_key: must match keys use to create TGW attachment, IGW, GWLB endpoint or other resources- next_hop_type: internet_gateway, nat_gateway, transit_gateway_attachment or gwlbe_endpointExample:vpcs = { example_vpc = { name = "example-spoke-vpc" cidr = "10.104.0.0/16" nacls = { trusted_path_monitoring = { name = "trusted-path-monitoring" rules = { allow_inbound = { rule_number = 300 egress = false protocol = "-1" rule_action = "allow" cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0" from_port = null to_port = null } } } } security_groups = { example_vm = { name = "example_vm" rules = { all_outbound = { description = "Permit All traffic outbound" type = "egress", from_port = "0", to_port = "0", protocol = "-1" cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"] } } } } subnets = { "10.104.0.0/24" = { az = "eu-central-1a", subnet_group = "vm", nacl = null } "10.104.128.0/24" = { az = "eu-central-1b", subnet_group = "vm", nacl = null } } routes = { vm_default = { vpc = "app1_vpc" subnet_group = "app1_vm" to_cidr = "0.0.0.0/0" next_hop_key = "app1" next_hop_type = "transit_gateway_attachment" } } } } | map(object({ name = string cidr = string nacls = map(object({ name = string rules = map(object({ rule_number = number egress = bool protocol = string rule_action = string cidr_block = string from_port = string to_port = string })) })) security_groups = any subnets = map(object({ az = string subnet_group = string nacl = string })) routes = map(object({ vpc = string subnet_group = string to_cidr = string next_hop_key = string next_hop_type = string })) })) | {} | no |
Outputs
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| application_load_balancers | FQDNs of Application Load Balancers |
| network_load_balancers | FQDNs of Network Load Balancers. |