Strata Cloud Manager API Best Practices
The Strata Cloud Manager (SCM) API provides a unified and consistent framework for automating the management and monitoring of your Palo Alto Networks security infrastructure.
Follow these best practices to ensure optimal performance, stability, and security for your integrations.
Authentication and Security
The SCM API uses the OAuth 2.0 Client Credentials flow for authentication. These practices are critical for application stability and security.
Token Management Best Practices
- Implement a caching mechanism to reuse access tokens across all SCM API interactions.
- Request an access token once and reuse it for all SCM API calls until it expires (typically after 15 minutes).
- Implement a token caching mechanism that automatically refreshes the token only when it is nearing expiration or when an API request returns a 401 Unauthorized response.
The following sample script demonstrates how to acquire an access token, cache it, reuse it for subsequent SCM API calls, and automatically refresh it when necessary:
import time
import requests
from typing import List, Dict, Any
TOKEN_URL = "https://auth.apps.paloaltonetworks.com/oauth2/access_token"
CLIENT_ID = "<YOUR_CLIENT_ID>"
CLIENT_SECRET = "<YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET>"
HOST = "api.strata.paloaltonetworks.com"
PROTOCOL = "https"
SCOPE = "tsg_id:<YOUR_TSG_ID>"
token_cache = {
"access_token": None,
"expires_at": 0
}
def get_access_token():
"""
Generate an access token for SCM.
"""
# Check if a token exists and is still valid (with a 60-second buffer for safety)
if token_cache["access_token"] and time.time() < token_cache["expires_at"] - 60:
return token_cache["access_token"]
else:
# If no valid token, request a new one
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
"Accept": "application/json",
}
try:
response = requests.post(
TOKEN_URL,
headers=headers,
data={
"grant_type": "client_credentials",
"client_id": CLIENT_ID,
"client_secret": CLIENT_SECRET,
"scope": SCOPE
}
)
# Raise an exception for 4xx or 5xx status codes
response.raise_for_status()
token_data = response.json()
token_cache["access_token"] = token_data["access_token"]
# Calculate absolute expiration time: Current Time + lifetime of token
token_cache["expires_at"] = time.time() + token_data["expires_in"]
return token_cache["access_token"]
except requests.RequestException as e:
print(f"Token retrieval failed: {e}")
if e.response is not None:
print(f" Status: {e.response.status_code}, Body: {e.response.text}")
return None
def get_devices() -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""
Retrieve the list of devices from SCM.
"""
token = get_access_token()
# Construct the endpoint path for getting devices
path = f"{PROTOCOL}://{HOST}/config/setup/v1/devices"
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {token}",
"Accept": "application/json",
}
try:
# Perform the GET request with a timeout to prevent hanging
response = requests.get(path, headers=headers, timeout=10)
response.raise_for_status()
json_response = response.json()
devices = json_response.get("data", [])
if not devices:
print("No devices found.")
return devices
except Exception as e:
print(f"Failed to retrieve devices: {e}")
return []
# Main Execution Block
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("Fetching Device Details...")
device_list = get_devices()
if device_list:
print(f"{'DEVICE NAME':<20} | {'SERIAL NUMBER':<20}")
print("-" * 45)
for device in device_list:
name = device.get("display_name", "Unknown")
serial = device.get("serial_number", "N/A")
print(f"{name:<20} | {serial:<20}")
- Adhere to these practices for service account management.
-
Grant service accounts only the minimum permissions required to perform their intended functions (principle of least privilege).
-
Remove or restrict access on service accounts immediately when no longer needed.
-
Regenerate your client secrets periodically in Strata Cloud Manager to reduce the risk of credential compromise.
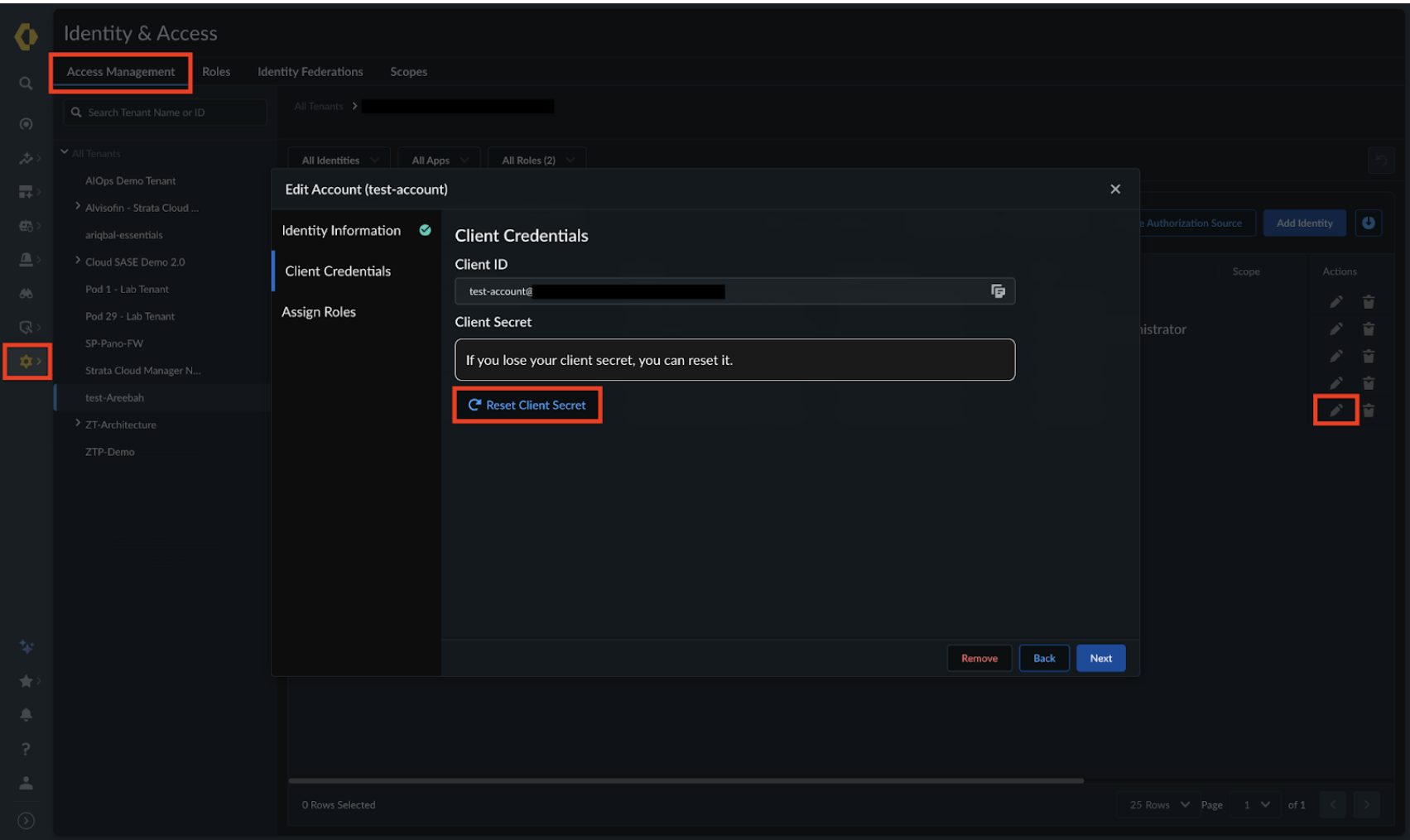
-
Never embed client secrets directly in source code. Instead, store the credentials securely using environment variables or a dedicated secret management system.
-
For example, you could use a JSON file to store the application’s SCM API configuration, with sensitive values referenced from environment variables rather than hardcoded.
{
"auth_url": "https://auth.apps.paloaltonetworks.com/oauth2/access_token",
"client_id": "<YOUR CLIENT ID>",
"client_secret": "<YOUR CLIENT SECRET>",
"host": "api.strata.paloaltonetworks.com",
"protocol": "https",
"scope": "tsg_id:<YOUR_TSG_ID>",
}
Configuration and Automation Workflow
Note: When automating configuration changes, ensure your process is robust.
Enforce consistent ordering of operations
Maintain a consistent sequence of operations to handle dependencies effectively. By ensuring prerequisites such as folder existence are met before executing subsequent actions, such as creating a security rule, you prevent avoidable API failures.
Data Handling
Efficient data exchange minimizes latency and reduces the load on both your script and the SCM API service.
-
Use standard JSON format and validate responses
- Request Bodies: Ensure your request body is formatted as JSON, and set the header to Content-Type: application/json.
- Response Handling: Expect standard JSON objects, often with nested structures. It is critical to validate the response by parsing it before processing, such as checking for empty values or ensuring that all the required fields are present.
-
Use filters to retrieve only relevant data
- Many SCM endpoints support query parameters such as name, folder, snippet, and more. Use these filters to retrieve only the data you need, avoiding the overhead of fetching large datasets and filtering them locally. For example, instead of retrieving all security rules, request only the rules within a specific folder.
GET /config/security/v1/security-rules?folder=Test
- Implement pagination for large datasets
- When retrieving large datasets, the SCM API uses limit and offset parameters, with a default limit of 200 items per page.
- Ensure your script loops through all pages to collect the complete set of results.
def get_scm_data(path: str, token: str, offset: int = 0, limit: int = 200, **scope) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
"""
Fetches all items from the SCM API using automatic pagination.
Args:
path (str): The API endpoint URL.
token (str): The OAuth2 access token. It is highly recommended to
handle token generation and refresh logic outside
this function.
offset (int): Starting index for pagination (default 0).
limit (int): Number of items to fetch per request (default 200).
**scope: Scope filters such as folder='Shared', snippet='MySnippet',
or device='MyDevice'. Defaults to folder='All' if no scope is provided.
Returns:
List[Dict[str, Any]]: A complete list of all items retrieved.
"""
all_items = []
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {token}",
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Accept": "application/json",
}
while True:
# Prepare parameters: Combine pagination with user-provided scope filters
params = {
"limit": limit,
"offset": offset,
"folder": "All"
}
print(f"\nFetching items {offset} to {offset + limit}...")
try:
# Execute the GET request
response = requests.get(path, headers=headers, params=params)
# This will raise an error for 4xx or 5xx responses
response.raise_for_status()
json_response = response.json()
items = json_response.get("data", [])
# No more data to fetch
if not items:
break
all_items.extend(items)
# --- OPTIONAL: Process or Log items ---
# You can customize this loop to extract specific fields or log progress.
for item in items:
item_name = item.get('name', 'N/A')
print(f" > Name: {item_name}")
# If the number of items returned is less than the limit, we have
# reached the end of the data set (last page).
if len(items) < limit:
break
# Increment the offset for the next API call
offset += limit
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"Error fetching data: {e}")
break
print(f"\nRetrieved {len(all_items)} total objects.")
return all_items
# Example Usage
if __name__ == "__main__":
results = get_scm_data("https://api.strata.paloaltonetworks.com/config/objects/v1/applications", token=t, scope="folder='Test'")
Script Reliability and Logging
Reliable SCM automation requires robust error handling, detailed logging, and proactive monitoring to diagnose issues quickly.
-
Perform a health check before executing a large automation task
- Perform a lightweight SCM API health check—such as listing a set of devices or retrieving a specific job—before executing large automation tasks to verify API availability, authentication validity, and connectivity.
-
Configure explicit timeouts
- Set appropriate timeouts for all HTTP requests to prevent your automation script from hanging indefinitely if the SCM API service is slow or unresponsive. For example, configure a 30-second timeout on an SCM API request to ensure the script terminates or retries if the service does not respond in a timely manner.
response = requests.get(
<GET_REQUEST_PATH>,
headers=headers,
timeout=30 # timeout in 30 seconds
)
- Implement error logging
- Implement comprehensive error logging that captures the full response—including the status codes, response bodies, and more—for any unsuccessful SCM API response. This is helpful for distinguishing between application errors (such as invalid data) and network errors.
- The following example demonstrates how to implement logging when creating a folder:
def create_folder( token: str, folder_name: str,parent_folder: str, description: Optional[str] = None, labels: Optional[List[str]] = None, snippets: Optional[List[str]] = None,) -> bool:
"""
Creates a folder in SCM.
Args:
token (str): The OAuth2 access token. It is highly recommended to
handle token generation and refresh logic outside
this function.
folder_name (str): The name of the folder to create.
parent_folder (str): The parent folder name.
description (str, optional): Description of the folder.
labels (List[str], optional): Labels assigned to the folder.
snippets (List[str], optional): Snippets associated with the folder.
Returns:
True if the folder is successfully created (2xx),
False otherwise.
"""
# SCM folder creation endpoint
path = "https://api.strata.paloaltonetworks.com/config/setup/v1/folders"
# Request headers
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {token}",
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Accept": "application/json",
}
# Request payload
payload = {
"name": folder_name,
"parent": parent_folder,
"description": description,
"labels": labels,
"snippets": snippets,
}
try:
# Make the API request to create the folder
response = requests.post(url=path, headers=headers, json=payload, timeout=15)
if response.ok:
# Case 1: Folder successfully created (2xx response)
logging.info(f"Successfully created folder: {folder_name}")
return True
else:
# Case 2: SCM responded, but returned an error (4xx / 5xx)
logging.error(
f"\nSCM API Error: Failed to Create Folder '{folder_name}'\n"
f"Status Code: {response.status_code}\n"
f"Parent Folder: {parent_folder}\n"
f"Payload: {payload}\n"
f"Error Message: {response.text}"
)
return False
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
# Case 3: SCM did not respond at all (network, timeout, DNS, TLS issues)
logging.error(f"Network Error: Could not reach SCM API. Details: {e}")
return False
# Example Usage
if __name__ == "__main__":
create_folder(token="<YOUR_TOKEN>", folder_name="<NEW_FOLDER>", parent_folder="<YOUR PARENT FOLDER>")