Access Tokens
To obtain an access token using Authentication Service, you must have already created at least one TSG and created a service account that has role-access assigned to it. When you did these things, you obtained:
- A TSG ID, which you use to identify the scope of the access token.
- A Client ID
- A Client Secret
Using this information, you can use POST /oauth2/access_token to create an access token. Be aware that:
-
The FQDN for the authentication service is different from the rest of the SASE APIs. It is:
https://auth.apps.paloaltonetworks.com -
This API uses basic auth. Use your Client ID for the username, and Client Secret for the password.
-
Use the
scopefield to provide the TSG ID.
For example:
curl -d "grant_type=client_credentials&scope=tsg_id:<tsg_id>" \
-u <client_id>:<client_secret> \
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
-X POST https://auth.apps.paloaltonetworks.com/oauth2/access_token
Note: The service account that you use to authenticate this request must belong to the TSG that
you identify on the scope field. See Acess Token Scopes for more information.
Access tokens have a lifespan of 15 minutes.
Check your access token credentials
If your access token is incorrect, the API request may not go through, and the resulting error indicates an invalid authorization code.
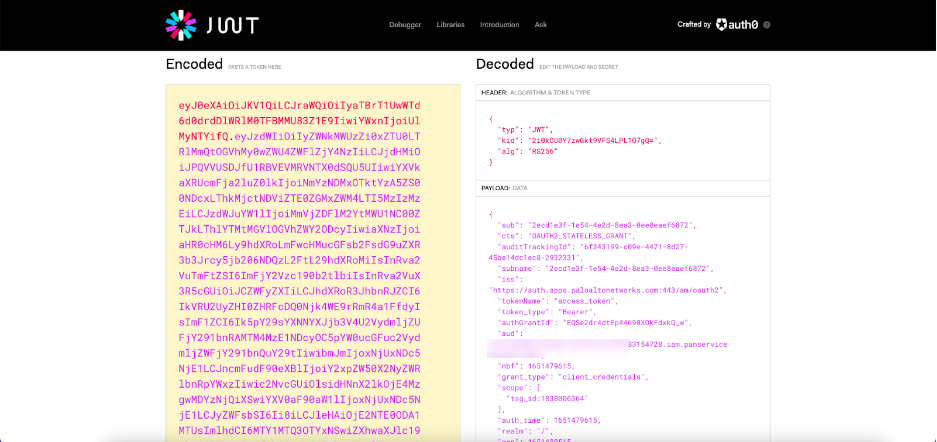
You can check your access token's credentials by pasting the access token into https://jwt.io/ . This decodes the token to determine whether the actual set of credentials matches the set of credentials present in the access token.
The example below shows an encoded access token and the same access token decoded. The decoded access token shows that the TSG_ID is 1838006364.